What is Macular Degeneration?
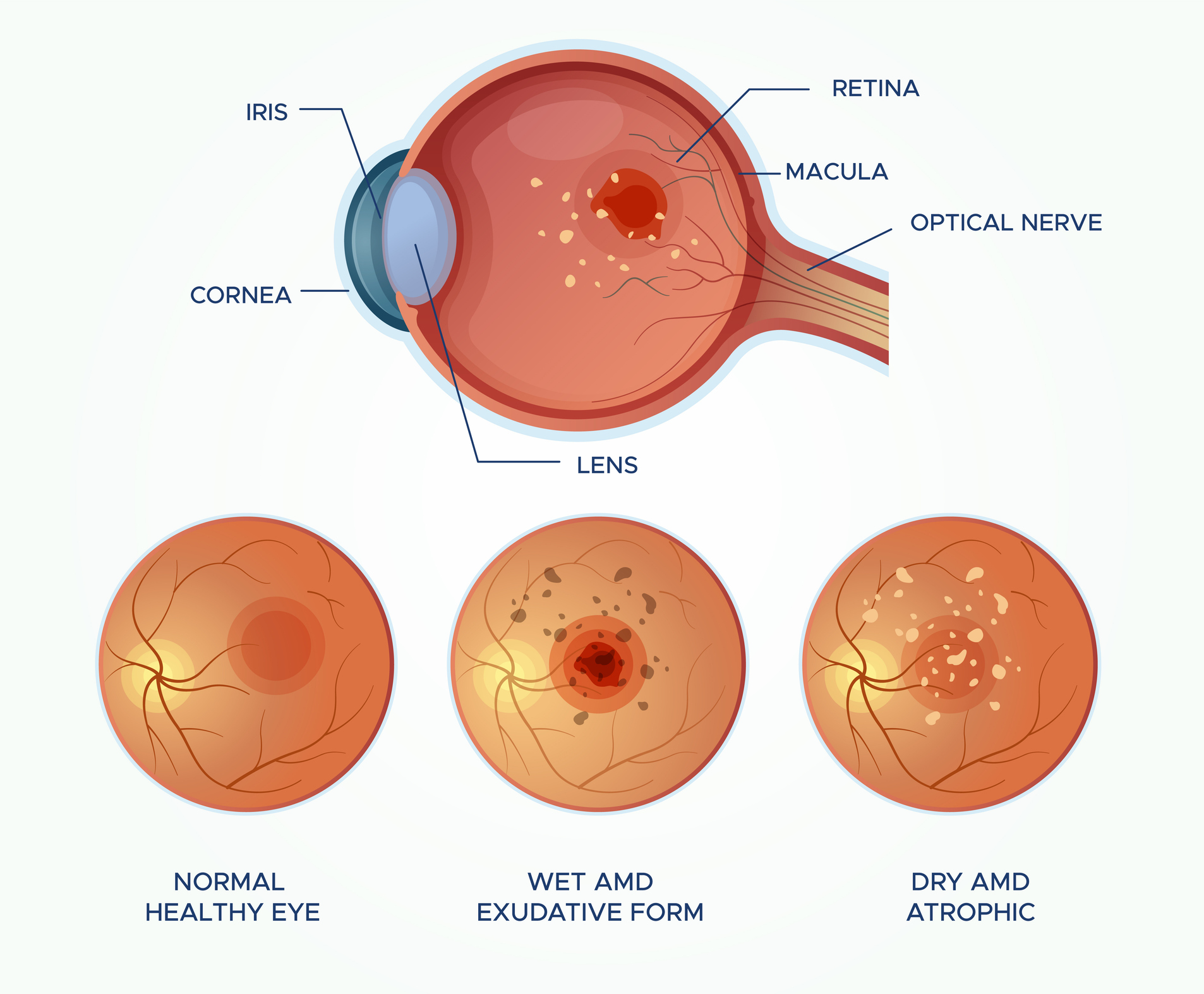
The macula is a small area in the retina at the back of the eye that allows you to see fine details clearly and perform activities such as reading and driving. Macular degeneration is the deterioration or breakdown of the macula. It reduces vision in the central part of the retina; however, it does not affect the eye’s side or peripheral vision. Most people first develop the dry form of AMD which is caused by the formation of yellow drusen deposits under the macula (the central part of your retina). These deposits cause your macula to gradually dry out and weaken.
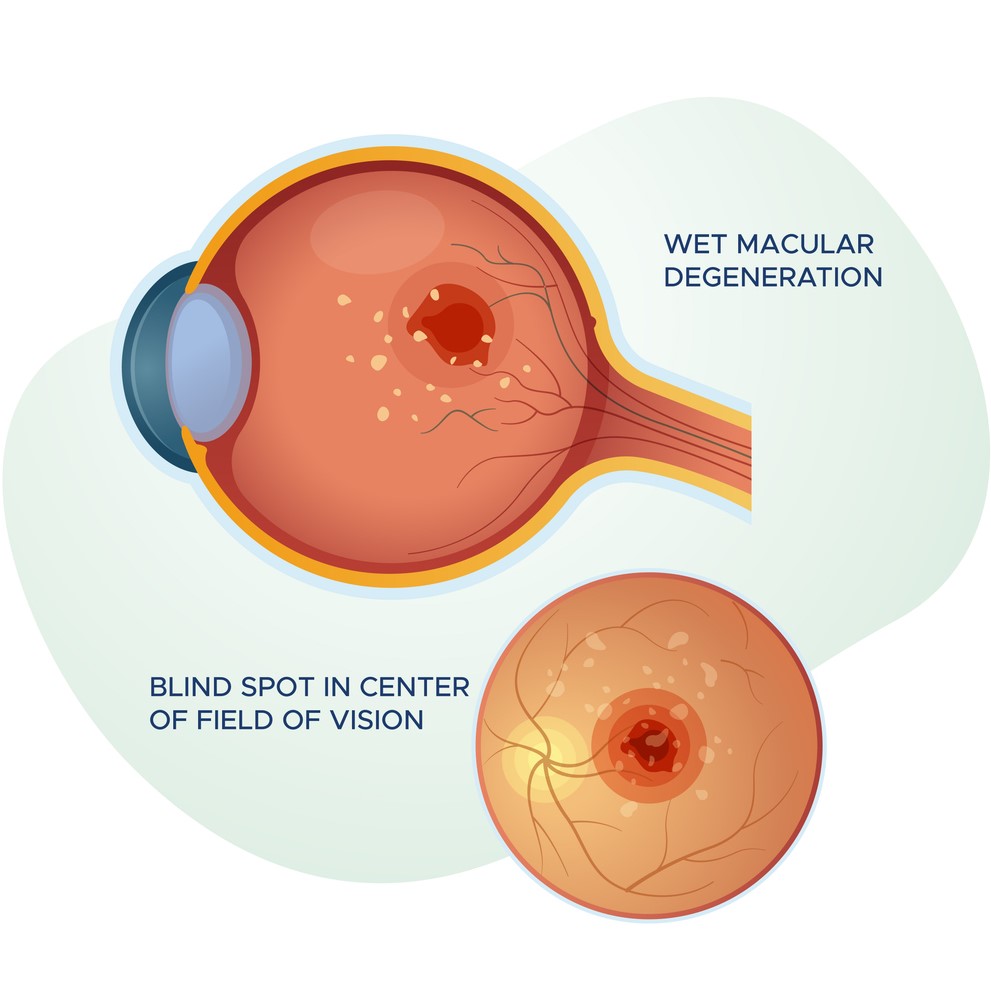
What are the types of Macular Degeneration?
There are two types of macular degeneration:
- Dry macular degeneration, which is caused by the macula breaking down and thinning with age
- Wet macular degeneration, which is caused by blood vessels leaking into the macula
Macular Degeneration Variations
Risk Factors for Macular Degeneration
You are at greater risk of developing macular degeneration if you:
- Smoke
- Are a woman
- Are overweight
- Are far-sighted
- Have light-colored eyes
- Have uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Are exposed to sunlight for long periods without eye protection
- Have a family history of macular degeneration
Signs and Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
When you are developing AMD, you may notice:
- Blurred vision
- Straight lines appearing wavy
- Objects appearing smaller than they are
- A gray, dark area in the center of your vision
- Colors appear paler than they are

Macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD)- is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field.
How can You Treat Macular Degeneration?
Patients with wet macular degeneration often require consultation with a retina specialist. Wet AMD occurs when abnormal blood vessels form under your retina. These delicate structures can leak blood or fluid into the retina causing rapid vision damage. There are new treatments including Avastin & Lucentis which have revolutionized care.



















































































































